Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, resulting from various sources such as industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and the burning of fossil fuels. Air pollution control is essential to mitigate the adverse effects on human health, ecosystems, and climate. By implementing effective control measures and utilizing air pollution control equipment, we can reduce the emission of pollutants and improve the quality of the air we breathe. Read More…
Anguil Environmental provides highly-engineered, environmental equipment and service solutions that help clients solve complex industrial air pollution control and wastewater treatment challenges across the globe. Anguil air pollution control systems include thermal and catalytic oxidation technologies for compliance with VOC, HAP and odor regulations.
Dürr CTS Inc. is a leading global supplier of environmental solutions and engineered products tailored to meet customers' industrial process requirements. We offer a complete portfolio of air pollution control technologies including scrubbers, wet electrostatic precipitators, thermal and catalytic oxidizers, and solvent recovery systems.

The CMM Group provides design and build, and technical engineering services for VOC emission control, odor abatement solutions and energy recovery systems. CMM Aftermarket Services team provides preventive maintenance and inspection services, controls upgrades, retrofit and rebuild services to extend the life of existing equipment. For small or large, complex projects, The CMM Group’s extensive ...
Meet stringent environmental regulations with Ducon's complete line of the most advanced air pollution control equipment: cyclones, scrubbers, incinerators, electrostatic precipitators, activated carbon absorbers, gas absorption towers, flue gas desulfurization, chemical strippers, NOx & VOC Control, etc.
We are Process Combustion Corporation, and we specialize in designing, engineering, and delivering advanced air pollution control solutions for industrial and commercial operations that demand reliable environmental compliance and long-term performance. Our work centers on helping manufacturers reduce harmful emissions, control particulate matter, and manage volatile organic compounds through...
More Air Pollution Control Equipment Manufacturers
Air Pollution Control Equipment
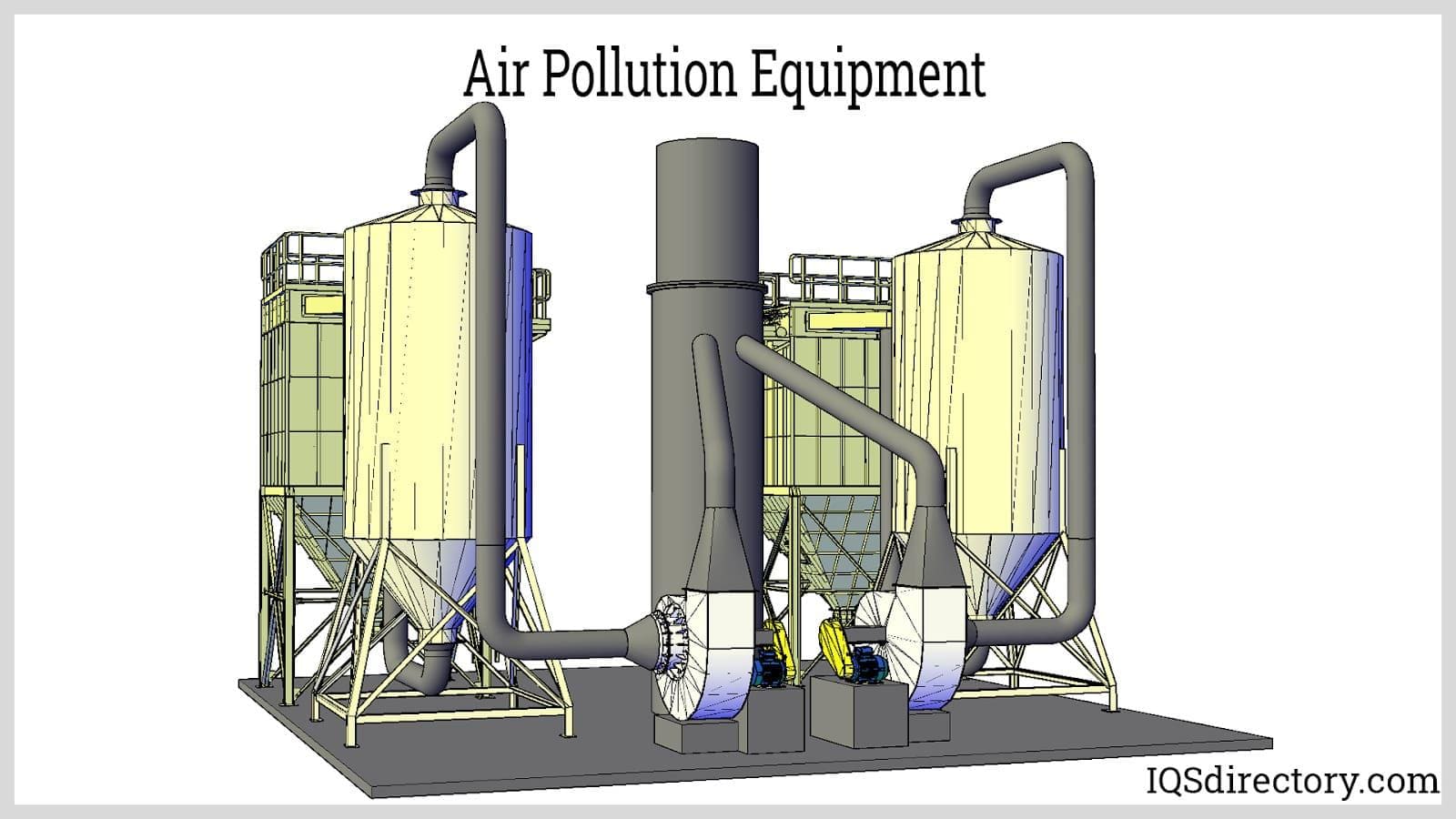
Air pollution control equipment comprises a comprehensive suite of engineered technologies and industrial solutions designed to reduce, capture, or eliminate hazardous airborne contaminants from industrial, commercial, and even residential air streams. As environmental regulations such as the EPA’s Clean Air Act become increasingly stringent and corporate sustainability goals take center stage, selecting the optimal air pollution control system is vital for organizations aiming to ensure regulatory compliance, improve workplace air quality, and minimize negative impacts on the environment.
Whether you are an environmental manager seeking to lower emissions, a plant operator striving for cleaner indoor air quality, or a purchasing agent vetting the best emission control technologies for your facility, understanding the range of available air pollution control equipment—and their capabilities, benefits, and decision criteria—can drive smarter investments and more sustainable operations. This guide explores the leading types of air pollution control equipment, their applications, benefits, and essential selection factors so you can make an informed choice tailored to your industry’s needs.
Types of Air Pollution Control Equipment
There are several types of air pollution control equipment, each engineered with unique pollutant removal mechanisms, operational advantages, and some limitations. The most common and effective solutions include scrubbers, dust collectors, oxidizers, and mist collectors. Understanding their individual strengths, how they work, and their ideal use cases is crucial for matching your emission profile with the right technology.
Scrubbers
Scrubbers are advanced air pollution control devices specifically designed to remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases through the introduction of a scrubbing liquid or sorbent into the exhaust stream. This interaction facilitates the removal, capture, and neutralization of targeted contaminants via mechanisms such as absorption, adsorption, or chemical reactions. Scrubbers are integral to industries with exhaust streams containing high concentrations of gaseous pollutants or acidic gases, such as power plants, refineries, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceutical plants, pulp and paper mills, steel mills, and waste incinerators.
Scrubbers are particularly effective at controlling and reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrogen chloride (HCl), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and particulate matter (PM). Many facilities utilize scrubbers to achieve compliance with the U.S. EPA’s National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP), meet local and state air quality standards, and reduce the risk of hefty environmental fines.
Operators may choose between wet scrubbers (ideal for acid gas removal or flue gas desulfurization), dry scrubbers (effective for incineration and waste-to-energy plants), or semi-dry systems that offer a middle ground. Each technology is engineered for specific applications—wet scrubbers excel at controlling water-soluble gases, while dry scrubbers are favored when water use must be minimized. Hybrid and multi-stage scrubber systems are increasingly popular for facilities with complex emission profiles.
Despite their versatility, scrubber technology has some limitations. High energy consumption can increase operational costs, as the process of dispersing scrubber liquids or reagents into the exhaust stream requires significant energy input. Additionally, wet scrubbers generate a liquid waste stream that must be managed to prevent secondary environmental harm. This waste stream, often containing captured pollutants, demands careful treatment and disposal. Furthermore, scrubbers may be less effective at capturing ultra-fine particulate matter or volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sometimes requiring supplementary technologies.
Looking for ways to improve scrubber efficiency or reduce long-term operational costs? Ask about the latest low-energy scrubber designs, hybrid systems, and advanced liquid waste handling solutions tailored to your industry.
Scrubber manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation, developing more energy-efficient designs and advanced automation for process optimization. Modern systems feature improved reagent delivery, corrosion-resistant materials, and enhanced control over pH and temperature to maximize pollutant capture. Some even integrate real-time emissions monitoring, enabling facilities to respond rapidly to process changes and ensure ongoing compliance. These advancements support a cleaner, safer workplace and help companies achieve ambitious sustainability goals.
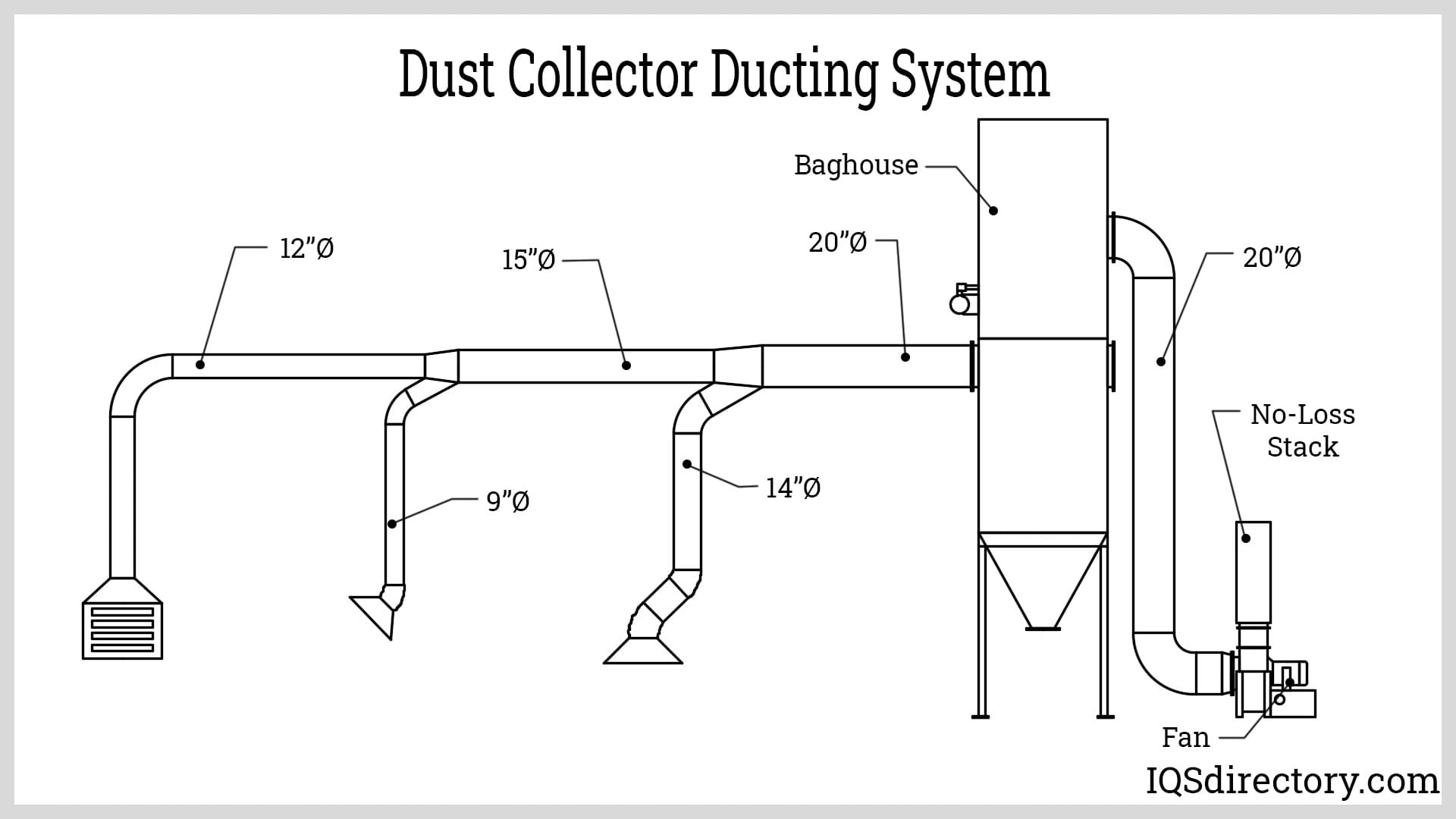
Dust Collectors
Dust collectors are critical air pollution control devices for removing particulate matter from air streams generated by manufacturing, processing, and material handling operations. They are engineered to capture fine dust, powders, metal shavings, wood chips, and other airborne particles, improving facility air quality and protecting worker health.
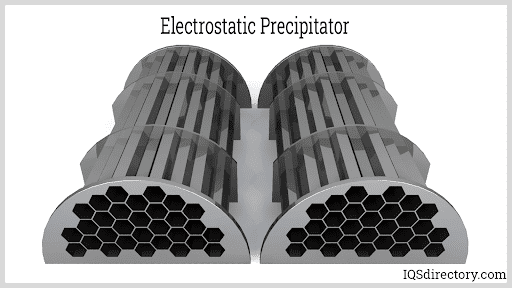
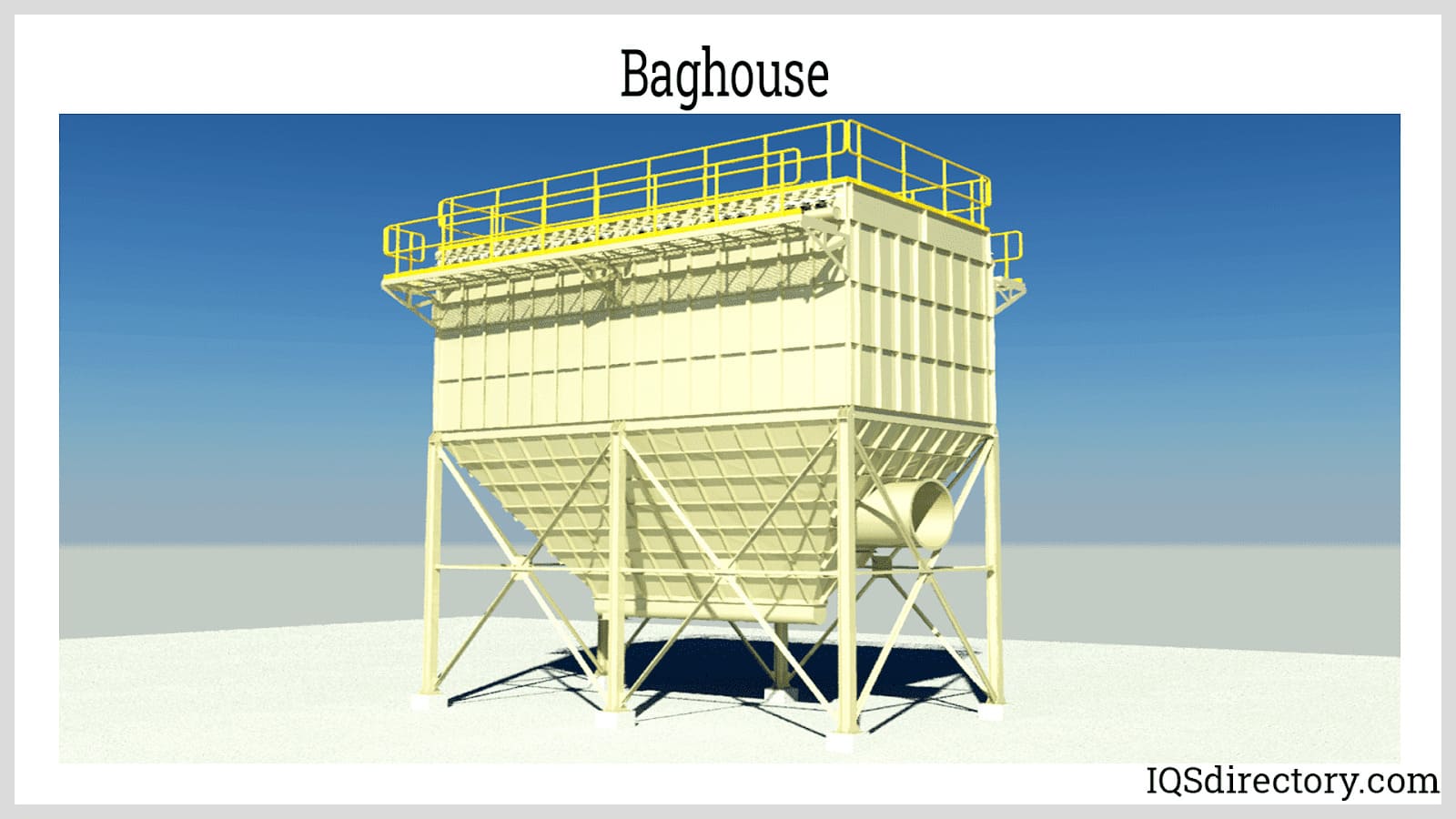
Modern dust collectors are essential in industries such as woodworking, metal fabrication, cement production, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and agriculture. These systems use various filtration technologies—including baghouse filters, cartridge collectors, cyclone separators, and electrostatic precipitators (ESPs)—to address a wide range of particulate sizes and concentrations.
Key benefits of industrial dust collectors include improved workplace safety (by reducing inhalation of hazardous dust particles), compliance with occupational health standards, protection of sensitive equipment, and reduced housekeeping and maintenance costs. Facilities using HEPA or ULPA filtration can achieve exceptionally high particle removal efficiencies, often exceeding 99.97% for sub-micron dust.
Thanks to technological advancements, today’s dust collectors feature high-efficiency filter media, automated pulse-jet cleaning, variable frequency drives (VFDs), and integrated sensors for real-time performance monitoring. These innovations lengthen filter life, minimize maintenance downtime, and optimize energy consumption.
Considering a dust collection system for your manufacturing plant? Explore advanced options such as HEPA filtration, self-cleaning filters, modular designs, and integrated air quality monitoring for maximum workplace safety and regulatory compliance.
For facilities with combustible dust, explosion protection features—like spark arrestors, isolation valves, and explosion vents—are crucial. Always ensure your dust collection system is designed to meet NFPA and OSHA requirements for combustible dust hazard mitigation.
Oxidizers
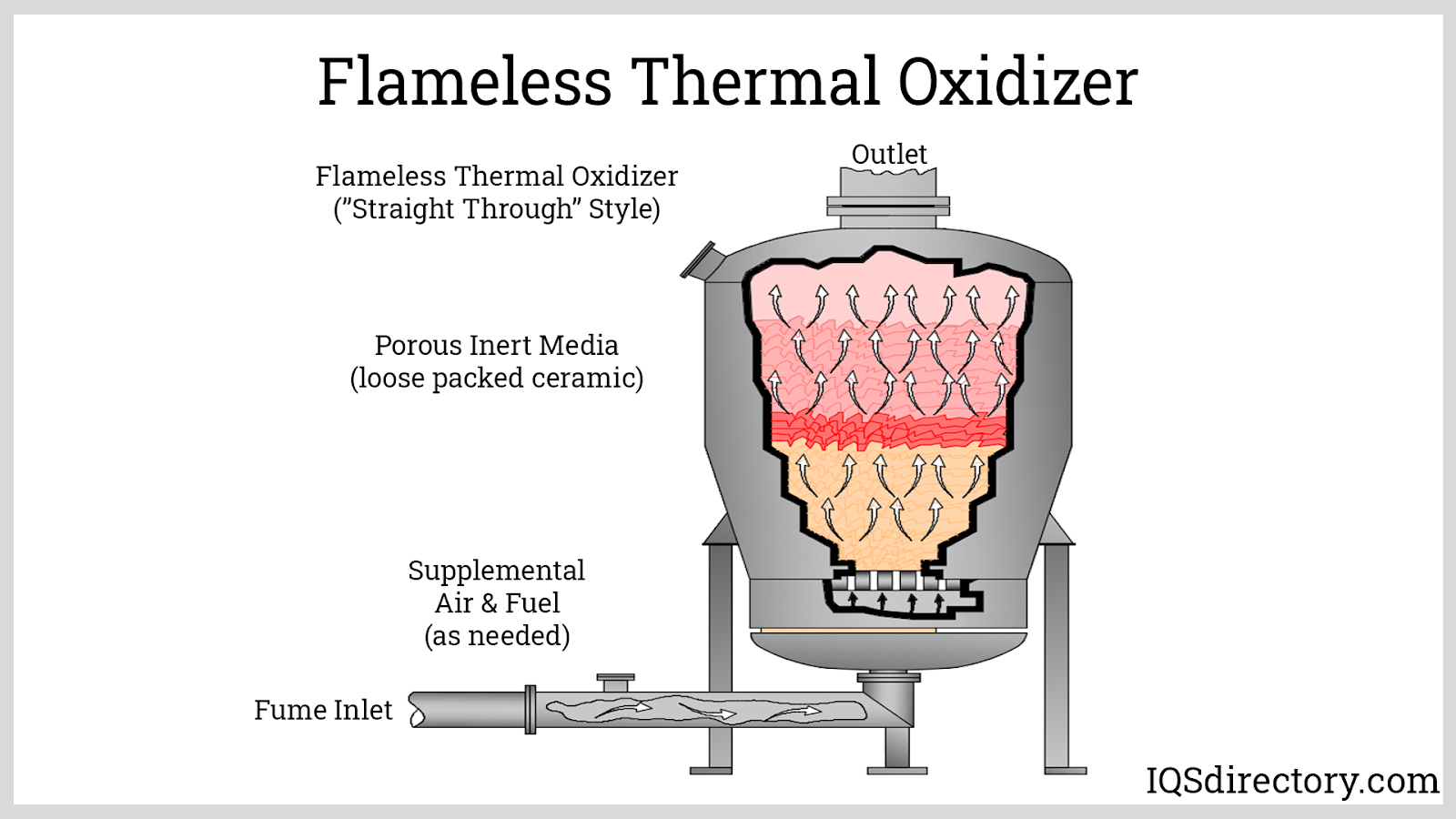
Oxidizers are sophisticated air pollution control devices targeting gaseous pollutants, particularly volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). These systems use high temperatures, in the presence of oxygen, to oxidize harmful compounds into non-toxic byproducts such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor.
Industries that generate VOC-rich exhaust—such as chemical manufacturing, printing, painting, surface coating, food processing, and pharmaceutical production—rely on oxidizers to achieve regulatory compliance and minimize health risks. There are several types of oxidizers, including thermal oxidizers, catalytic oxidizers, and regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs). Each offers distinct advantages in terms of energy efficiency, destruction removal efficiency (DRE), and operational cost.
While oxidizers are highly effective, they require significant energy to maintain the high temperatures needed for complete oxidation, potentially increasing fuel costs. Some oxidation processes may also produce secondary emissions, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) or carbon monoxide (CO), depending on exhaust composition and combustion conditions. This underscores the importance of robust system design and advanced controls.
Curious about how regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) can cut energy costs and boost destruction removal efficiency? Compare RTO, catalytic, and direct-fired oxidizer systems based on your facility’s emission profile and energy goals.
Recent advances in oxidizer technology include heat recovery systems (to reclaim energy from exhaust streams), next-generation catalysts for lower operating temperatures, and integrated automation for emission monitoring and process optimization. These improvements support lower operating costs, higher efficiency, and reduced environmental impact.
When evaluating oxidizers, consider factors such as exhaust flow rate, VOC/HAP concentration, required DRE, available fuel sources, and potential for heat recovery. Properly sizing and specifying your oxidizer ensures compliance and operational efficiency.
Mist Collectors
Mist collectors—also known as oil mist eliminators or mist filtration systems—are engineered to capture and remove liquid droplets, aerosols, and mists from industrial air streams. Key applications include metalworking fluid mists, oil mist from machining, coolant mists, and fumes from plastic injection molding or die casting. By using mechanisms like impaction, interception, and coalescence, these systems prevent slippery surfaces, protect workers, and maintain clean production areas.
Mist collectors typically employ filtration media, centrifugal force, or electrostatic precipitation to separate droplets from the air stream. Captured liquids are drained for proper disposal or recycling, supporting resource conservation and cost savings.
Challenges for mist collectors include handling high-viscosity or sticky mists, which may require specialized filter coatings or pre-filtration stages. Regular maintenance—such as cleaning or replacing filters—is crucial to prevent pressure drops and performance issues. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency and mist re-entrainment.
To address these challenges, manufacturers are innovating with enhanced filtration media, self-cleaning mechanisms, and smart sensors to monitor filter status and optimize maintenance schedules. Some systems now offer automatic filter cleaning and remote performance tracking.
Looking for the right mist collector for CNC machining, metalworking operations, or plastic processing? Evaluate centrifugal, electrostatic, and media-type mist collectors for your specific application and air quality requirements.
Benefits of Air Pollution Control Equipment
Air pollution control equipment delivers wide-ranging benefits for individuals, businesses, and the environment. At the individual and community level, these systems protect health by reducing exposure to airborne toxins, allergens, and carcinogens, thereby lowering the risk of respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic health conditions. Cleaner air also improves quality of life, supporting outdoor activities and healthy living.
For businesses, investing in air pollution control systems ensures regulatory compliance, minimizes liability, and protects against costly fines. Organizations using advanced emission control technologies often enjoy enhanced brand reputation, as environmental stewardship is increasingly valued by customers, partners, and investors. Cleaner workplace air boosts employee morale, reduces absenteeism, and increases productivity.
On a global scale, air pollution control equipment is a frontline defense against climate change, reducing the emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) and hazardous pollutants. These solutions support resource conservation, preserve ecosystems, and contribute to biodiversity by limiting acid rain, smog, and toxic deposition. By adopting advanced air pollution control technology, industries pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Still wondering, “How will air pollution control devices help my facility meet EPA regulations?” or “What ROI can I expect from upgrading my emission control system?” Contact our experts for a customized assessment and explore case studies tailored to your sector.
Applications of Air Pollution Control Equipment
Air pollution control equipment finds essential use across numerous industries and sectors, with each facing unique emission challenges. In industrial manufacturing, precision systems manage emissions from metalworking, foundries, chemical processing, cement plants, glass manufacturing, pulp and paper, and food processing. Advanced particulate collectors, wet scrubbers, catalytic oxidizers, and electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are often customized to address specific pollutants—from metal dust and silica to VOCs and acid gases.
In power generation, both utility-scale and distributed energy plants rely on high-efficiency pollution controls to treat exhaust from fossil fuel combustion—including coal, natural gas, and biomass. Key solutions include flue gas desulfurization (FGD), selective catalytic reduction (SCR), ESPs, and baghouses, which work together to slash SO2, NOx, and particulate emissions for cleaner energy production.
The automotive sector depends on advanced emission control systems such as catalytic converters, diesel particulate filters (DPFs), and SCR systems to meet ever-tightening emission standards. These technologies reduce vehicle exhaust pollutants including carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), NOx, and fine particulates, enabling cleaner transportation solutions.
Municipal waste incineration and hazardous waste treatment facilities utilize robust air pollution control solutions to capture dioxins, furans, mercury, and heavy metals, protecting local air quality and ensuring adherence to strict government regulations.
Beyond heavy industry, air pollution control equipment is vital for enhancing indoor air quality in offices, schools, hospitals, and homes. HVAC systems equipped with HEPA or ULPA filtration and advanced ventilation technologies remove indoor contaminants, fostering safer and more comfortable environments.
From factory floors to energy plants, automotive fleets to commercial buildings, air pollution control technology is a versatile, mission-critical asset for compliance, sustainability, and public health.
Are you searching for air pollution control solutions for a specific industry, such as food processing, foundries, or pharmaceutical manufacturing? Explore our sector-specific application guides for targeted recommendations, best practices, and compliance checklists.
How to Select Appropriate Air Pollution Control Equipment
Selecting the optimal air pollution control equipment requires a methodical approach rooted in a thorough understanding of your facility’s emissions, operational needs, and long-term compliance objectives. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure you make an informed decision:
- Identify Pollutant Types and Sources:
Determine the primary and secondary pollutants generated by your processes—such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). Map emission sources (e.g., boilers, paint lines, furnaces) to tailor solutions. - Analyze Emission Volume and Concentration:
Calculate airflow rates (CFM), pollutant concentrations, and total emission loads. This data is critical for proper equipment sizing and selection. - Match Technology to Pollutant Profile:
Use ESPs or baghouse filters for particulate control, SCR for NOx reduction, scrubbers for acid gases, and oxidizers for VOC and HAP abatement. Consider combinations or hybrid systems for complex emission streams. - Evaluate Compliance and Efficiency Requirements:
Ensure the system meets all relevant EPA, state, and local standards (such as MACT, NESHAP, NSPS). Target removal efficiencies (e.g., 99% PM, 95% VOC) appropriate for your industry and regulatory context. - Assess Operational and Life-Cycle Costs:
Balance initial capital investment against long-term savings from energy efficiency, reduced maintenance, and compliance avoidance. Factor in consumables (filters, reagents, catalysts) and potential energy recovery. - Consider Installation and Maintenance Needs:
Evaluate facility layout, available space, integration with existing systems, and staff capacity for routine maintenance. Choose suppliers offering strong technical support, training, and after-sales service. - Plan for Scalability and Future Regulations:
Select systems that can be upgraded or expanded to meet stricter future standards or increased production volumes, such as modular baghouses or add-on catalytic stages.
Need help comparing emission control technologies, cost structures, or compliance guarantees? Reach out for personalized consultation, detailed equipment specifications, or a cost-benefit analysis.
Common buyer questions include:
- What is the best air pollution control equipment for my industry or process?
- How do I evaluate dust collectors versus wet scrubbers for particulate removal?
- What are the total operating and maintenance costs over the equipment lifecycle?
- How can I ensure my system will be compliant with evolving EPA and local regulations?
- Can my facility integrate heat recovery or energy-saving features into the emission control system?
Looking for guidance on technology selection, vendor comparison, or system integration? Our experts can provide tailored recommendations and benchmarking data for your unique operational requirements.
The Future of Air Pollution Control Equipment
The future of air pollution control equipment is shaped by rapid technological innovation, increasing regulatory demands, and a growing focus on sustainability. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and smart automation is transforming how facilities monitor and manage emissions, enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and automated process optimization for maximum system efficiency and uptime.
Emerging filtration technologies, such as nanofiber filters and advanced ceramic media, promise unprecedented pollutant capture rates and longer service life. Hybrid emission control systems—combining scrubbers, ESPs, and catalytic stages—are gaining traction for multi-pollutant abatement and reduced footprint.
Sustainability is driving the adoption of renewable energy-powered air pollution control equipment, such as solar-assisted oxidizers and energy-efficient dust collection systems with regenerative drives. Facilities are increasingly looking to minimize their carbon footprint by integrating waste heat recovery and resource recycling into emission control strategies.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to revolutionize emission monitoring and operational optimization. These technologies enable adaptive control, process tuning, and early warning for maintenance needs—reducing downtime and maximizing compliance.
Collaboration among equipment manufacturers, research institutions, and regulatory agencies is fostering breakthroughs in pollution control science and policy, with the goal of achieving cleaner air, lower costs, and enhanced system flexibility.
Curious about how smart, connected air pollution control systems can transform your facility’s operations and sustainability profile? Explore our resource center for the latest trends, case studies, and emerging solutions.
Choosing the Right Air Pollution Control Equipment Supplier
Selecting a reputable, experienced supplier is critical to the success of your air pollution control project. Our comprehensive directory of air pollution control companies simplifies the vendor evaluation process. Each supplier’s business profile page details their product range, technical expertise, industry focus, and service capabilities. Use the integrated contact form on each profile to request detailed product information, technical support, or a custom quote.
Our patented website previewer allows you to quickly compare manufacturers’ offerings, certifications, and capabilities. Once you have narrowed down your options, use our streamlined Request for Quote (RFQ) form to contact multiple suppliers with a single inquiry—saving you time and ensuring a competitive bidding process.
When evaluating suppliers, consider the following critical factors:
- Proven experience in your industry and with your specific pollutants or processes
- Range of technologies offered (e.g., scrubbers, oxidizers, dust collectors, mist collectors, ESPs)
- Availability of after-sales support, maintenance services, and operator training
- Customer references, project case studies, and documented compliance track records
- Ability to deliver custom-engineered or turnkey solutions tailored to your unique requirements
- Responsiveness to technical inquiries and willingness to provide on-site assessments or pilot testing
A strong supplier will act as a partner—guiding you through system selection, installation, commissioning, and ongoing operation. Prioritize vendors who offer robust service agreements, prompt technical support, and access to replacement parts and consumables.
Check out our Dust Collector website
Check out our Parts Washers website
Ready to take the next step? Use our directory to compare air pollution control equipment manufacturers, request quotes, or schedule a consultation and ensure your facility is equipped for regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and environmental leadership.
What are the main types of air pollution control equipment?
The most common types of air pollution control equipment include scrubbers, dust collectors, oxidizers, and mist collectors. Each is engineered to target specific pollutants and applications, such as particulate matter, acid gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and liquid aerosols.
How do scrubbers work, and what pollutants do they remove?
Scrubbers remove contaminants from industrial exhaust streams by introducing a scrubbing liquid or sorbent. This process captures and neutralizes pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrogen chloride (HCl), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and particulate matter. Scrubbers are widely used in industries like power plants, refineries, and manufacturing facilities.
What are the benefits of using air pollution control equipment?
Air pollution control equipment protects human health, ensures regulatory compliance, reduces the risk of fines, improves workplace air quality, enhances brand reputation, and supports sustainability goals by minimizing the release of hazardous pollutants and greenhouse gases.
How should I select the right air pollution control equipment for my facility?
Selecting the right equipment involves identifying your facility’s pollutants and emission sources, analyzing emission volume, matching technology to pollutant profile, ensuring regulatory compliance, considering operational and life-cycle costs, evaluating installation and maintenance requirements, and planning for future scalability and regulations.
In which industries is air pollution control equipment commonly used?
Air pollution control equipment is used in industries such as manufacturing, power generation, automotive, waste incineration, hazardous waste treatment, and in non-industrial environments like offices, hospitals, schools, and commercial buildings to improve indoor and outdoor air quality.
What are the latest technological advancements in air pollution control equipment?
Recent advancements include integration of IoT sensors, smart automation, nanofiber filtration media, hybrid multi-stage systems, renewable energy-powered solutions, AI-driven process optimization, real-time emissions monitoring, and advanced heat recovery for improved efficiency and sustainability.
What should I look for in an air pollution control equipment supplier?
Choose suppliers with proven experience in your industry, a wide range of technologies, strong after-sales support, customer references, the ability to provide custom solutions, and responsiveness to technical needs. A good supplier offers partnership from selection to ongoing support and maintenance.




 Air Compressors
Air Compressors  Air Filters
Air Filters Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Blowers
Blowers Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment
Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services