Air pollution has become an increasingly concerning issue in recent years, with various industries and human activities contributing to the degradation of air quality. As a result, various methods and technologies have been developed to control air pollution, including electrostatic precipitators (ESPs). In this article, we’ll provide an overview of ESPs, including their operation, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Read More…
Anguil Environmental provides highly-engineered, environmental equipment and service solutions that help clients solve complex industrial air pollution control and wastewater treatment challenges across the globe. Anguil air pollution control systems include thermal and catalytic oxidation technologies for compliance with VOC, HAP and odor regulations.
Dürr CTS Inc. is a leading global supplier of environmental solutions and engineered products tailored to meet customers' industrial process requirements. We offer a complete portfolio of air pollution control technologies including scrubbers, wet electrostatic precipitators, thermal and catalytic oxidizers, and solvent recovery systems.

The CMM Group provides design and build, and technical engineering services for VOC emission control, odor abatement solutions and energy recovery systems. CMM Aftermarket Services team provides preventive maintenance and inspection services, controls upgrades, retrofit and rebuild services to extend the life of existing equipment. For small or large, complex projects, The CMM Group’s extensive ...
Meet stringent environmental regulations with Ducon's complete line of the most advanced air pollution control equipment: cyclones, scrubbers, incinerators, electrostatic precipitators, activated carbon absorbers, gas absorption towers, flue gas desulfurization, chemical strippers, NOx & VOC Control, etc.
We are Process Combustion Corporation, and we specialize in designing, engineering, and delivering advanced air pollution control solutions for industrial and commercial operations that demand reliable environmental compliance and long-term performance. Our work centers on helping manufacturers reduce harmful emissions, control particulate matter, and manage volatile organic compounds through...
More Electrostatic Precipitator Manufacturers
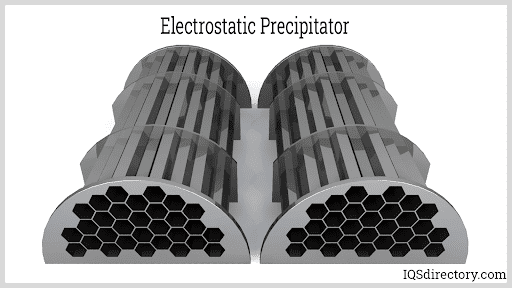
What are Electrostatic Precipitators?
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are advanced air pollution control devices engineered for the high-efficiency removal of particulate matter (PM) from industrial exhaust gases. Utilizing electrostatic forces, ESP systems are essential for industries that generate large volumes of airborne contaminants, including power generation, cement manufacturing, steel production, chemical processing, waste incineration, pulp and paper, petroleum refining, and more.
By integrating electrostatic precipitators into their emission control strategies, facilities can significantly reduce air pollution, comply with stringent environmental regulations, and improve overall air quality. ESPs are pivotal for achieving regulatory compliance under frameworks such as the Clean Air Act, and for meeting New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) and National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP).

How do Electrostatic Precipitators Work?
Wondering how ESPs capture dust and airborne particles so effectively? Electrostatic precipitators operate via a highly efficient two-stage process, making them one of the most reliable technologies for industrial air filtration and particulate collection.
Stage 1: Electrostatic Charging
In the initial phase, the ESP system uses discharge electrodes to create a strong electrical field. As the polluted gas stream enters the precipitator chamber, fine airborne particles such as dust, smoke, and mist are exposed to a corona discharge. This process ionizes the gas, imparting an electrical charge to the particles, typically negative.
Stage 2: Particle Collection
As the charged particles travel through the ESP, they are attracted to and adhere to oppositely charged collector plates (or collection electrodes). The now-cleaned gas flows out of the device, while the accumulated particulate matter remains on the plates. This stage is highly effective for both coarse and submicron particles, including fly ash, soot, and acid mists.
To maintain collection efficiency, ESPs employ mechanical rappers or vibration mechanisms that periodically dislodge the accumulated dust from the plates. The dislodged particles fall into hoppers below, where they can be safely collected and disposed of or recycled, depending on the process requirements.
This method allows for continuous operation with minimal pressure drop, ensuring low energy consumption and consistent air quality control.

Manufacturing of Electrostatic Precipitators
The manufacturing process for electrostatic precipitators involves advanced engineering, precision fabrication, and rigorous quality assurance to deliver reliable, high-performing equipment. Leading electrostatic precipitator manufacturers design ESPs tailored to a wide range of industrial air pollution control applications, ensuring compatibility with different process parameters, dust loadings, temperatures, and corrosive environments.
Key Components of Electrostatic Precipitators
An ESP consists of several precision-engineered components that work together to maximize particulate removal efficiency and system durability:
- Discharge Electrodes: High-voltage electrodes that create the electrical field and generate corona discharge, enabling particle charging.
- Collector Plates (Collection Electrodes): Large, grounded metal plates that capture charged dust and particulate matter.
- Rappers or Vibrators: Mechanical systems that periodically clean the collector plates by striking or vibrating them, ensuring continuous operation.
- High-Voltage Power Supply: Specialized equipment that delivers the required voltage (often from tens to hundreds of kilovolts) to maintain the electrical field.
- Hoppers: Robust containers located beneath the ESP, designed to collect and store dust and particulate matter for safe disposal or recycling.
- Gas Distribution Devices: Structures that ensure even gas flow and prevent turbulent zones, optimizing collection efficiency.
- Insulators and Enclosures: Electrical insulators and weatherproof enclosures that protect sensitive components and maintain safety during operation.

Manufacturing Process Steps
Building a reliable ESP system requires a sequential process guided by industry standards and best practices:
- 1. ESP System Design: Engineers analyze process requirements—such as gas volume, particulate characteristics, temperature, moisture, and corrosiveness—to create custom ESP designs. Computer modeling is often used to optimize the layout, gas flow, and electrical parameters for maximum collection efficiency and minimal pressure drop.
- 2. Fabrication: Components are manufactured from selected materials (such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum) using cutting, welding, bending, and precision machining. Advanced surface treatments—like galvanizing, powder coating, or anti-corrosion linings—are applied to enhance durability and ensure long service life, especially in harsh industrial environments.
- 3. Assembly: The fabricated components are assembled into the ESP housing. This phase includes installation of electrodes, collector plates, rappers, hoppers, insulators, access doors, and electrical systems. Meticulous attention to detail is crucial to prevent leaks, electrical shorts, or maintenance issues.
- 4. Electrical Integration: High-voltage power supplies and control panels are integrated, and safety interlocks are installed to ensure safe and reliable ESP operation. Automation and remote monitoring capabilities may be added for large-scale or critical facilities.
- 5. Testing and Quality Assurance: Each ESP undergoes rigorous performance testing before delivery. Tests include verification of collection efficiency, power consumption, pressure drop, mechanical integrity, and compliance with regulatory standards such as EPA NSPS and NESHAP. Instruments like particle counters, emission analyzers, and oscilloscopes are used for in-depth validation.
- 6. Installation and Commissioning: On-site installation is performed by experienced technicians, followed by system commissioning to calibrate controls and ensure optimal performance in live operating conditions.
Wondering how to select the right materials or optimize ESP sizing for your application? Jump to our buyer’s guide below for key decision-making factors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ESPs
Advantages of Electrostatic Precipitators
- Superior Collection Efficiency: ESPs can remove up to 99.9% of particulate matter, including fine dust, fly ash, smog, mists, and even some bioaerosols. Their ability to capture submicron particles (as small as 0.01 microns) makes them ideal for meeting ultra-low emission limits.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, ESPs offer low operational expenses due to minimal pressure drop and reduced energy consumption compared to baghouses or wet scrubbers.
- High Capacity & Scalability: ESPs are easily scaled for small, medium, or large industrial plants—capable of handling gas flows from 1,000 m3/hr to over 1,000,000 m3/hr.
- Continuous Operation: Unlike many filtration systems, ESPs can operate continuously with periodic cleaning, resulting in minimal downtime and consistent air quality control.
- Durability: ESPs feature robust construction with corrosion-resistant materials, providing decades of reliable service in demanding industrial environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for dry and wet applications—dry ESPs for dust and ash, and wet ESPs for sticky, moist, or corrosive particulates.
- Minimal Maintenance: With no moving parts inside the gas stream and automated cleaning mechanisms, ESPs require infrequent maintenance, reducing downtime and labor costs.
Disadvantages of Electrostatic Precipitators
- High Initial Investment: ESPs can be more expensive to purchase and install than other air pollution control systems, such as cyclone separators or cartridge filters.
- Specialized Maintenance: Skilled technicians are required for troubleshooting, routine maintenance, and electrical work, which can add to long-term operational costs.
- Requires High-Voltage Power: The need for dedicated high-voltage power supplies increases energy consumption and can impact overall plant electrical design.
- Potential Ozone Generation: The corona discharge process in ESPs may produce small amounts of ozone, which must be monitored and controlled to avoid health or environmental impacts.
- Limitations with Certain Pollutants: ESPs are generally less effective at removing gaseous pollutants, vapors, or very sticky substances. For comprehensive control, they are often combined with dust collectors or wet scrubbers.
- Performance Sensitivity: ESP collection efficiency can be affected by variations in particle resistivity, humidity, and process gas characteristics, requiring careful system design and tuning.
Curious about how ESPs compare to baghouses, cartridge filters, or wet scrubbers? Explore our emission control systems comparison guide.
Applications of Electrostatic Precipitators
Electrostatic precipitators are deployed across a diverse range of industries and processes where precise air pollution control is essential. Common ESP use cases include:
- Power Generation: Coal-fired power plants, biomass boilers, and waste-to-energy facilities use ESPs to capture fly ash, soot, and acid mist, ensuring compliance with particulate emission limits.
- Cement Manufacturing: ESPs control dust emissions from cement kilns, clinker coolers, and grinding mills, reducing visible emissions and improving workplace safety.
- Steel and Metal Production: Steel mills, aluminum smelters, and foundries use ESPs for removing metallic fumes, dust, and slag particles from furnace exhaust streams.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Processing: ESPs capture fine particulates, catalyst residues, and mist from reactors, dryers, and acid plants.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: ESPs reduce particulate emissions from recovery boilers and lime kilns, supporting regulatory compliance and sustainable manufacturing.
- Waste Incineration: Municipal and hazardous waste incinerators use ESPs to control fly ash, toxic metals, and dioxins in exhaust gases.
- Food Processing and Manufacturing: ESPs remove oil mist, flour dust, and process particulates, ensuring product quality and worker safety.
- Other Industries: ESPs are also found in glass manufacturing, ceramics, battery production, mining, asphalt plants, and many other industrial sectors where particulate control is required.
Want to know which type of ESP is best for your industry? Consult our supplier selection guide below.
ESPs for Specialized Applications
In addition to standard industrial applications, electrostatic precipitators are also used for:
- Indoor Air Purification: ESP-based air cleaners are utilized in commercial buildings, hospitals, and cleanrooms to control ultrafine particulates, allergens, and even viruses.
- Automotive and Transportation: ESPs are being researched for emission control in diesel engines, marine vessels, and locomotives.
- Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing: Ultra-clean ESPs remove particulate contamination from process gases in microelectronics fabrication.
Still have questions about ESP suitability for your process? Reach out to a supplier for expert guidance.
Choosing the Right Electrostatic Precipitator Supplier
Selecting the ideal electrostatic precipitator manufacturer or supplier is crucial for achieving long-term success with your air pollution control system. The right partner will offer not only reliable products but also technical expertise, customization, after-sales support, and ongoing maintenance solutions.
Key Considerations When Selecting an ESP Supplier
- Industry Experience: Does the supplier have proven experience delivering ESPs for your specific industry and application (e.g., power generation, cement, steel, chemicals)?
- Customization and Engineering: Can the manufacturer tailor ESP design, sizing, and materials to your process requirements—gas volume, temperature, dust concentration, and corrosiveness?
- Regulatory Compliance: Are their products designed and tested to meet local and international emission standards (EPA, EU, etc.)?
- Aftermarket Support: Do they provide installation, commissioning, operator training, spare parts, and field maintenance services?
- Warranty and Reliability: What warranties, performance guarantees, and maintenance packages are offered?
- References and Case Studies: Can the supplier provide customer references, testimonials, or case studies demonstrating successful ESP installations?
- Cost and ROI: Does the solution balance initial investment with operating cost savings, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability?
- Innovation and Technology: Are advanced features available—such as remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, or integration with plant control systems?
How to Compare ESP Suppliers
To ensure you achieve the best results, compare several electrostatic precipitator suppliers using our comprehensive directory. Each supplier’s profile highlights their unique capabilities, certifications, and areas of expertise. Use the profile pages to quickly learn what each company specializes in, and reach out directly using our convenient contact forms to request detailed information or a custom quote.
Ready to start your supplier search? Use our patented website previewer and easy-to-use RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple ESP companies at once—streamlining your vendor evaluation process.
Need a step-by-step guide for specifying your next ESP? Consider the following action points:
- Define your process requirements: maximum gas flow, temperature, dust loading, and pollutant characteristics.
- Identify regulatory limits and reporting requirements for particulate emissions in your jurisdiction.
- Shortlist suppliers with proven relevant experience and robust technical support.
- Request detailed proposals—including system sizing, materials, performance guarantees, and life-cycle costs.
- Evaluate after-sales support, installation, and field service offerings.
- Confirm references and review case studies for similar successful installations.
- Complete a total cost analysis, factoring in energy use, maintenance, and expected equipment lifespan.
Still have questions or need further assistance? Contact our team or explore our emission control solutions for more resources.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electrostatic Precipitators
What are the main types of ESPs?
Dry ESPs are used for dust and dry particulate removal, while wet ESPs are designed for capturing sticky, moist, or corrosive particles. Plate-type and tubular ESPs are common configurations, with each suited for specific industrial applications.
How do ESPs compare to other dust collectors?
ESPs offer higher efficiency for fine particle removal, lower pressure drop, and continuous operation compared to baghouses or cartridge filters. However, baghouses are sometimes preferred for sticky or fibrous dust, while wet scrubbers are chosen for gas-phase pollutants.
How is ESP performance measured?
Key metrics include collection efficiency (%), outlet particulate concentration (mg/Nm3), power consumption (kWh), and pressure drop (Pa or inWC). Routine stack testing and continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) are used for regulatory reporting.
What maintenance is required for ESPs?
Maintenance typically includes periodic inspection and cleaning of electrodes and plates, checking power supplies and insulators, replacing worn rappers, and recalibrating control panels. Regular service ensures reliable operation and regulatory compliance.
Can ESPs be retrofitted to existing plants?
Yes, many suppliers offer custom retrofit solutions for older plants to upgrade emission control performance and meet modern standards. Retrofitting may include new electrode designs, upgraded power supplies, automation, and improved rappers.
Have a specific question about ESP technology or installation? Contact us for expert advice.




 Air Compressors
Air Compressors  Air Filters
Air Filters Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Blowers
Blowers Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment
Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services